Good day and joyful Thursday! At this time we mark the 104th anniversary of the downing and demise of Baron Manfred von Richthofen (aka, “The Purple Baron”).
At this time I’ve a fast tackle a petition to Congress in addition to a quick(ish) explainer on how China thinks about cyber and the way it is likely to be utilized in a battle with Taiwan.
A Cheap Request
A bunch of former nationwide safety leaders has despatched one other letter to Congress, asking lawmakers to conduct a proper nationwide safety evaluation of any pending laws aimed toward “Massive Tech.” The signatories embody a former director of nationwide intelligence, secretary of protection, secretary of homeland safety, and commander of U.S. Cyber Command and director of the Nationwide Safety Company. That is like one other letter despatched late final yr on which I additionally commented.
Right here’s the crux of the most recent letter:
It is a pivotal second in trendy historical past. There’s a battle brewing between authoritarianism and democracy, and the previous is utilizing all of the instruments at its disposal, together with a broad disinformation marketing campaign and the specter of cyber-attacks, to convey a few change within the world order. … U.S. expertise platforms have already taken concrete steps to shine a light-weight on Russia’s actions to brutalize Ukraine. Via their efforts, the world is aware of what is actually occurring in cities from Mariupol to Kiev, undistorted by manipulation from Moscow. … Each in public and behind the scenes, these firms have rolled out built-in cyber defenses, quickly fused menace intelligence throughout services and products, and moved rapidly to dam malicious actors on their platforms. This partnership has resulted within the detection and disruption of a collection of serious safety threats from Russia and Belarus. … Within the face of those rising threats, U.S. policymakers should not inadvertently hamper the power of U.S. expertise platforms to counter rising disinformation and cybersecurity dangers, significantly because the West continues to depend on the size and attain of those companies to push again on the Kremlin. However lately proposed congressional laws would unintentionally curtail the power of those platforms to focus on disinformation efforts and safeguard the safety of their customers within the U.S. and globally.
Contemplating this, the authors make one request:
We name on the congressional committees with nationwide safety jurisdiction – together with the Armed Providers Committees, Intelligence Committees, and Homeland Safety Committees in each the Home and Senate – to conduct a evaluation of any laws that would hinder America’s key expertise firms within the combat towards cyber and nationwide safety dangers emanating from Russia’s and China’s rising digital authoritarianism. Such a evaluation would be certain that legislative proposals don’t improve our adversaries’ capabilities.
It’s apparent this letter is utilizing the state of affairs in Ukraine as a chance to push again on pending antitrust and different laws aimed toward “Massive Tech.” However that doesn’t imply the issues, or the request are unfounded (see my earlier commentary for extra particulars). In reality, it needs to be customary working process for these committees of jurisdiction to conduct primary nationwide safety evaluations of any laws that may materially have an effect on these pursuits, not to mention an trade that constitutes almost 10 % of American GDP.
The request on this letter just isn’t solely affordable, but additionally frequent sense. Some may rightly marvel why we even have these protection and intelligence committees in the event that they show unwilling to train oversight on points so central to their mission.
How China Thinks About Cyber
The occasions in Ukraine have me considering, particularly the shocking lack of large-scale Russian cyber operations which I’ve written on and spoken of with Steve and Jonah throughout this week’s Dispatch Dwell. A number of people, together with me, are questioning what classes China may take from these occasions and, as you noodle on them yourselves, I believed it’d be useful to provide a fast primer on how Beijing thinks about cyber operations and the way they is likely to be employed towards Taiwan.
The Individuals’s Liberation Army (PLA) views cyber means as an elemental characteristic of “informatized” wars, during which info is each “a website during which warfare happens” and “the central means to wage army battle.” Accordingly, Chinese language doctrine locates cyber throughout the bigger operational idea of knowledge operations (IO), which additionally consists of digital, area, and psychological warfare. Chinese language strategists say these are the important thing capabilities that have to be coordinated as strategic weapons to “paralyze the enemy’s operational system of programs” and “sabotage the enemy’s warfare command system of programs.” In different phrases: The PLA believes info is the vital useful resource on the trendy battlefield and that victory is achieved by guaranteeing one’s personal entry to this useful resource whereas denying it to the enemy. IO, then, is a broad operational idea centered on defending China’s capability to gather, use, and share info whereas additionally shaping its opponents’ perceptions and talent to finish these similar duties. Within the age of digitized knowledge, cyber means are essential to informatized warfare.
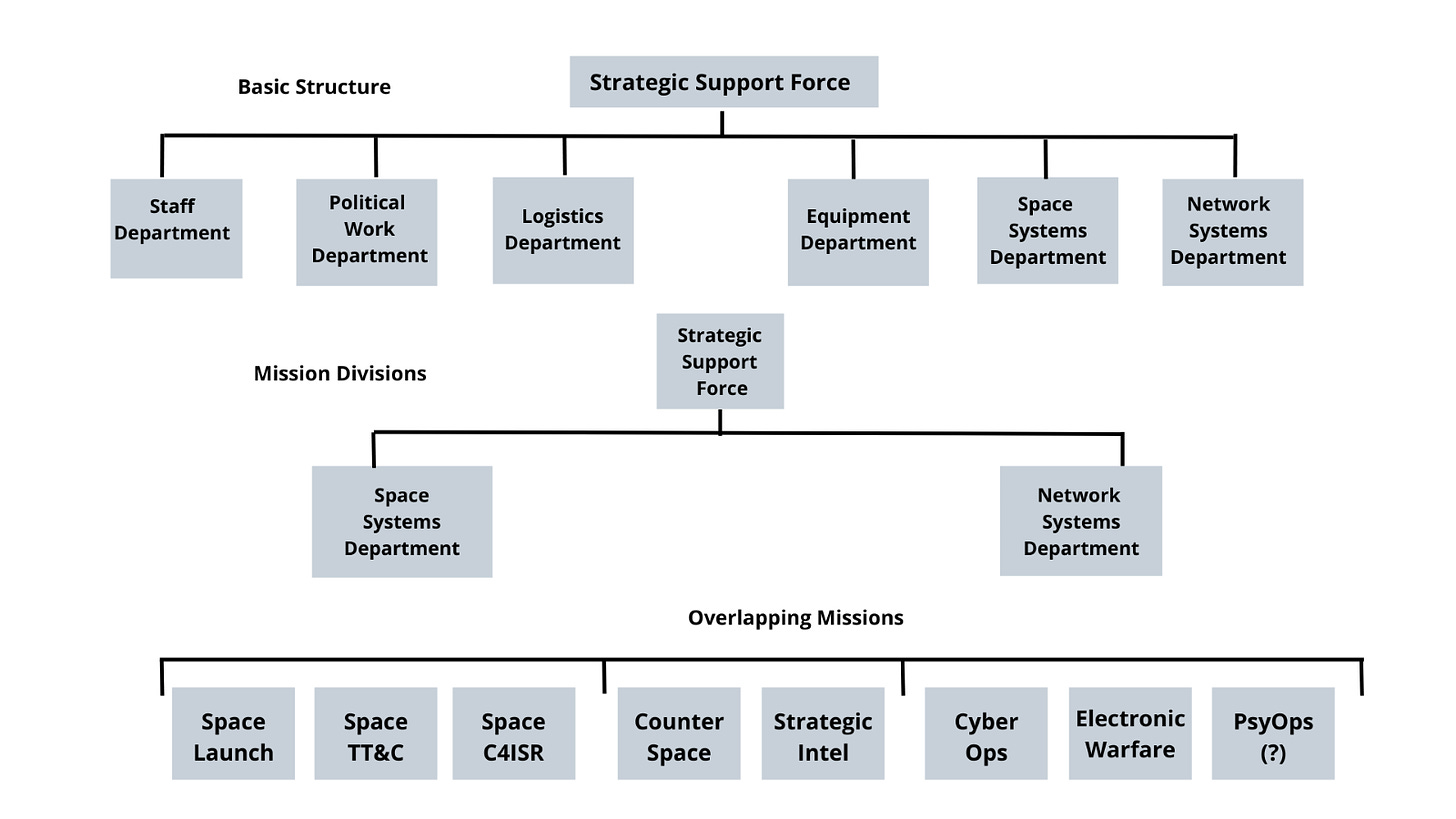
The PLA’s Strategic Help Power (SSF), established in December 2015 as a part of China’s intensive army reforms, has main accountability for cyber operations. The general drive construction and staffing of the SSF remains to be opaque, however we do have a primary sense of its operational group. The SSF consists of two mission fivisions—a House Techniques Division (SSD) and a Community Techniques Division (NSD). The SSD has three distinctive missions: area launch; area telemetry, monitoring, and command; and area command, management, communications, computer systems, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance. The NSD additionally has three missions: cyber operations, digital warfare, and psychological operations. Each the SSD and NSD share accountability for counterspace and strategic intelligence missions.
Earlier than this reform, the PLA had a discipline-centric construction during which particular person cyber, digital, area, and psychological warfare items had been organized by mission (i.e., defensive, offensive, or reconnaissance). Beneath this outdated construction, defensive cyber was dealt with by the previous Informatization Division, offensive cyber was carried out by the Fourth Division (often known as 4PLA), and the Third Division (often known as 3PLA) managed cyber espionage. The opposite warfare disciplines had been equally fractured. Because the PLA embraced new doctrines for contemporary warfare, it realized it should additionally modernize its drive construction to successfully prosecute these wars. To this finish, the SSF not solely unifies these formally disparate components but additionally is constructed round an crucial of “peacetime-wartime integration,” an idea that understands efficient cyber warfare doesn’t start with the onset of official hostilities; it’s as a substitute an never-ending exercise that should seamlessly transition between peacetime and wartime.
Pulling this all collectively: Chinese language planners consider it’s important to determine and preserve cyber superiority to allow the total spectrum of informatized warfare, to discourage opponents, and to handle escalation. However this superiority, within the minds of PLA planners, just isn’t one thing that’s solely seemed for within the early days of a battle, it is a bonus that have to be gained and leveraged now. It’s useful, then, to consider PLA cyber objectives, not as a listing of duties to be accomplished, however as a group of ceaseless actions that solely differ in depth based mostly on political necessities.
So, right here’s what I believe would be the key cyber goals if issues go sideways throughout the Taiwan Strait.
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance. Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) is an SSF core mission and underpins all different cyber actions. Chinese language hackers are continuously having access to Taiwan’s info programs and networks to raised perceive China’s targets. Mapping the island’s vital infrastructure and political-military command and management networks are important goals of those actions. For instance, in 2021 China hacked Taiwan’s in style Line messaging service to spy on high-level political officers, army personnel, and metropolis leaders. This had the tangible impact of giving the CCP essential perception into these communities and the intangible, however nonetheless essential, impact of undermining these communities’ confidence within the safety of their communications.
Operational preparation of the surroundings. The SSF can also be tasked with operational preparation of the surroundings (OPE). OPE is formally an indicator of American technique and doctrine, however its defining options are additionally current in Chinese language planning—significantly within the PLA’s “three warfares”: public-opinion warfare, psychological warfare, and authorized warfare. Cyber operations in assist of Chinese language OPE embody pre-positioning instruments and malicious code on susceptible networks, the event of detailed intelligence and targets associated to future army motion, and operations meant to have particular results on the attitudes and behaviors of Taiwan’s residents and authorities. All these actions are meant to create an surroundings that’s favorable to China’s objectives in peace and warfare.
Offensive cyberattacks on Taiwan. China’s hackers are additionally tasked with offensive cyberattacks on Taiwan—actions meant to govern, disrupt, or destroy networks, infrastructure, and each day life. Throughout peacetime, these operations assume the type of distributed denial of service, ransomware, and the distribution of different malware. In wartime, these cyberattacks can be extra aggressive. Chinese language hackers would attempt to disrupt, degrade, or destroy all the things from civilian telecommunications networks to army command and management programs. Air protection programs would go down, energy grids would go darkish, and important authorities companies would come to a grinding halt.
Deterring or slowing the American response. Deterring or slowing the American response in assist of Taiwan is one other key goal for the SSF. These operations can be extraordinarily delicate and extremely influenced by the political context during which they happen. In some ways, Chinese language informatized warfare doctrine is crafted particularly with the USA in view, and the SSF already has cyber plans for a number of situations. Regardless of the state of affairs, the broad purpose can be to undermine the USA’s confidence in its capability to decisively intervene on behalf of Taipei and its capability to take action.
If this all occurred tomorrow, how dangerous may or not it’s? Fairly dangerous.
Taiwan is catastrophically susceptible to Chinese language cyber aggression. The island’s vital infrastructure, authorities companies, and key army capabilities already endure between 20 million and 40 million cyber assaults each month, with the overwhelming majority of those coming from China. Chien Hung-wei, head of Taiwan’s Division of Cyber Safety, says he can defend towards most of those assaults however admits “severe” breaches repeatedly happen. “The operation of our authorities extremely depends on the web,” explains Chien. “Our vital infrastructure, similar to gasoline, water and electrical energy are extremely digitized, so we are able to simply fall sufferer if our community safety just isn’t sturdy sufficient.” This illustrates China’s chief cyber benefit—scale.
Concrete personnel and budgetary numbers regarding Beijing’s digital forces aren’t available in unclassified channels however estimates vary between 50,000 and 100,000 people (concerning the seating capability of the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum), with tons of of thousands and thousands of {dollars} at their disposal. No matter their precise workforce and funding, FBI Director Christopher Wray has stated that “right here within the US, [Chinese hackers have] unleash[ed] an enormous, refined program that’s greater than these of each different main nation mixed.” (Emphasis added.) It may be assumed, then, that comparable economies of scale can be employed towards considered one of Xi’s most coveted aspirations—China’s unification with Taiwan.
In early 2001, Taipei arrange the Nationwide Middle for Cyber Safety Know-how (NCCST), tasked to “set up the cyber safety safety mechanism and supply technical companies to authorities companies, together with prior-incident safety safety, during-incident early warning and responses, and post-incident recoveries and forensics.” Whereas the NCCST has made notable progress, it’s nowhere close to the maturity, dimension, or energy wanted for its mission. Relatedly, Taiwan is barely on the cusp of constructing the intragovernmental, trade, and worldwide partnerships mandatory for successfully participating and rolling again the deluge of hostile Chinese language efforts on-line.
None of those critiques are aimed toward Taipei’s needs or political will. They’re merely a recognition of a menace that even the USA, with its large assets and capabilities, is totally failing to mitigate. However hope just isn’t misplaced, and significant enhancements will be made within the close to time period that may dramatically shift the steadiness in favor of Taiwan.
However there are two concrete steps that we are able to take to make the state of affairs a lot better: Harden the homeland and tag staff with Taiwan.
First, the USA should proceed to harden itself towards Chinese language cyberthreats to the American homeland and army forces. Taiwan has little to no probability of efficiently deterring or stopping a Chinese language army assault with out American assist, and this help can be severely constrained if the USA doesn’t have a systemic, complete effort to shut our personal cybersecurity loopholes.
Trying past our borders, second, joint cyberwar workouts with Taiwan needs to be expanded in each frequency and scope. The primary of those workouts was held in 2019, but it surely was hosted by the American Institute in Taiwan—which represents U.S. pursuits on the island—not the U.S. army. It’s now time to synchronize our army cyber operations, as a result of it might be exactly these capabilities that may rely in a warfare with China. Whereas Beijing would definitely protest these workouts, they might not be an act of warfare and certain wouldn’t substantively threat upsetting right now’s delicate political equilibrium within the Taiwan Strait. Even when they did, this threat of rising tensions remains to be preferable to Taipei remaining unable to guard itself towards the legions of Chinese language army hackers arrayed towards it.
One other efficient however admittedly controversial motion can be for Taiwan to grant U.S. cyber forces direct entry to their programs for joint “lively threat-hunting” operations. These would contain U.S. and Taiwanese operators working facet by facet, crawling by way of the island’s many networks to search out and take away Chinese language (and different) hostile actors. Definitely, Taipei may very well be forgiven for any hesitation about permitting such broad entry to a international nation, however China is already in these networks, and bringing U.S. muscle to Taiwan’s cyber defenses may very well be the distinction between crumbling underneath a Chinese language offensive and maintaining sturdy defensive capabilities. The one various—making an attempt to seek out community vulnerabilities on the onset of battle—can be far too little, too late.
So, to conclude, cyber means are on the coronary heart of China’s rising army doctrine and can nearly absolutely characteristic closely in any assault on Taiwan. In reality, the PLA’s understanding of “peacetime-wartime integration” helps us to see Beijing’s ongoing cyber actions because the early levels of such an effort. Whereas Beijing is a formidable cyber adversary there are concrete steps that may be taken to safe the USA and our mates in Taiwan. Now we should take these steps.
That’s it for this version of The Present. Make sure you touch upon this submit and to share this article with your loved ones, mates, and followers. You too can observe me on Twitter (@KlonKitchen). Thanks for taking the time and I’ll see you subsequent week!