On the morning of Dec. 28, 1835, a single gunshot rang out within the central Florida wilderness. Chief Micanopy fired the preliminary shot earlier than 100 eighty Seminole warriors hidden within the shrubs opened up on 110 unsuspecting U.S. troopers.
Quickly after, 108 troopers had been lifeless. The Second Seminole Warfare had begun.
Fewer than 2,000 Seminole warriors would discover themselves dealing with an amazing military of 30,000 Individuals. It turned the longest, costliest and deadliest battle the US fought towards any Native American tribe. Though the Seminoles suffered heavy losses and plenty of had been compelled from their ancestral house, they by no means surrendered.
The Highway to Warfare
America and the Seminoles had already fought as soon as earlier than. Between 1817 and 1818, Normal Andrew Jackson led troops into Spanish Florida throughout the First Seminole Warfare. His forces attacked Seminole villages and Black Seminole settlements as they pursued escaped slaves from Georgia and different states.
Unable to defend the territory, Spain ceded Florida to the US in 1819. The U.S. took formal possession in 1821.
White settlers quickly flooded into Florida. They wished the fertile lands occupied by roughly 5,000 Seminoles in northern and central Florida. The Seminole nation had coalesced over the earlier many years from Creek, Hitchiti and Miccosukee peoples who migrated south.
Florida sheltered a whole lot of escaped slaves. Some lived in Black Seminole communities close to Native cities. Others had intermarried into Seminole households. Many had been born free in Florida. By the 1830s, Black Seminoles numbered a number of hundred. They’d kind a vital a part of the resistance.
In 1823, the U.S. authorities compelled Seminole leaders to signal the Treaty of Moultrie Creek. The treaty confined them to a four-million-acre reservation in central Florida. The federal government promised cash and provides to make sure their sovereignty. In return, white settlers may construct roads by way of the reservation and hunt for escaped slaves.
The treaty was violated virtually instantly. The federal government delivered provides late or in no way. White settlers stole Seminole cattle. They encroached on reservation lands continually. Slave hunters outright raided Seminole villages.
President Andrew Jackson then signed the Indian Elimination Act in 1830. The regulation mandated the relocation of all jap tribes, to be moved west of the Mississippi River. In 1832, U.S. negotiators met Seminole leaders at Payne’s Touchdown. They demanded the Seminoles abandon Florida fully. The Treaty of Payne’s Touchdown gave them three years to maneuver to Indian Territory in present-day Oklahoma.
Many Seminoles refused. Osceola, a younger Creek warrior, turned essentially the most vocal opponent. At one assembly, he stabbed his knife into the treaty doc. “My pores and skin is darkish, however not black!” he mentioned. “I’m an Indian, a Seminole. The white man shall not make me black. I’ll make the white man crimson with blood.”
The treaty said that Black Seminoles would stay in Florida. That meant slave hunters may reclaim them. For Osceola and plenty of others, that was unacceptable. By late 1835, conflict was inevitable.
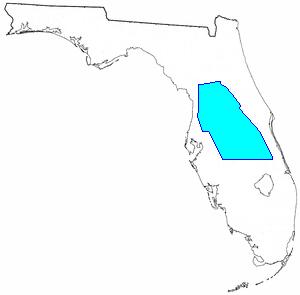
The Dade Bloodbath
Main Francis Langhorne Dade led 110 troopers north from Fort Brooke close to Tampa on Dec. 23, 1835. His command included troops from the 2nd and third Artillery and 4th Infantry. They marched towards Fort King close to present-day Ocala to bolster the garrison as tensions escalated.
Seminole scouts shadowed each step. Dade knew enemy warriors had been watching. He anticipated an ambush at every river crossing or within the thick woods. After 5 quiet days, he stopped posting flankers to look at the column’s sides.
Simply earlier than 8 a.m. on Dec. 28, Chief Micanopy fired. His bullet killed Dade immediately. 100 eighty warriors opened hearth from the palmettos and timber. The primary volley killed or wounded half of the American drive.
Captain George Gardiner took command. The survivors constructed a log breastwork. They managed to carry for hours. Then the Seminoles launched a closing assault within the afternoon.
By the tip of the engagement, 108 of the 110 troopers had been lifeless or dying. Personal Ransom Clarke and Personal Joseph Sprague survived with extreme wounds. A 3rd man escaped however died the following day.
Halpatter Tustenuggee helped plan the ambush. “We had been making ready for this greater than a 12 months,” he later mentioned. “Simply because the day was breaking, we moved out of the swamp into the pine-barren. I counted, by path of Jumper, 100 and eighty warriors.”
On the identical day, Osceola’s warriors attacked Fort King. They killed Indian Agent Wiley Thompson and 6 others. Thompson had been imposing Seminole removing. News of the massacres unfold throughout the nation. Individuals demanded army motion.

Guerrilla Warfare within the Swamps
Seminoles and Black Seminoles struck again laborious in early 1836. Warfare events raided plantations alongside Florida’s east coast and St. John’s River. By February, that they had attacked 21 plantations. Sugar mills burned. Enslaved individuals fled to affix the resistance. White settlers had been slaughtered.
Chief Micanopy led the general resistance. Osceola turned a strong conflict chief. Jumper, Alligator and Coacoochee commanded their very own warrior bands. Sam Jones, additionally known as Arpeika, led his forces from deep within the Everglades. Halleck Tustenuggee directed operations in central Florida. Black Seminole leaders John Caesar and John Horse commanded an estimated 300 to 400 Black fighters.
American numbers constructed up steadily all year long. In the meantime, a younger Lieutenant with orders to report on to the Commandant of the Marine Corps, Archibald Henderson, in Washington D.C. discovered a word pinned to his door.
The word learn, “Gone to Florida to struggle the Indians. Might be again when the conflict is over.”

Normal Thomas Jesup took command of all U.S. forces in late 1836. He famous the general racial undertones of the marketing campaign. “It is a negro, not an Indian conflict,” he warned. “If or not it’s not speedily put down, the south will really feel the consequences of it on their slave inhabitants.”
Fewer than 2,000 Seminole warriors confronted a U.S. drive that grew to 30,000 troops. The numbers meant little. Florida’s terrain gave the defenders the benefit. Swamps, sawgrass prairies and dense hammocks made standard army operations practically inconceivable. Summer season warmth and illness killed extra troopers than fight. Malaria and yellow fever in all probability prompted a lot of the 1,500 American deaths throughout the conflict.
The Seminoles hid their households on distant islands within the Everglades. Warriors struck American troops in unsuspecting ambushes. They disappeared into the terrain the place the American troopers could not comply with. They used feigned retreats to attract the pursuers into kill zones. They positioned themselves in dense tree islands surrounded by sawgrass and dust, forcing U.S. forces to advance throughout uncovered floor.
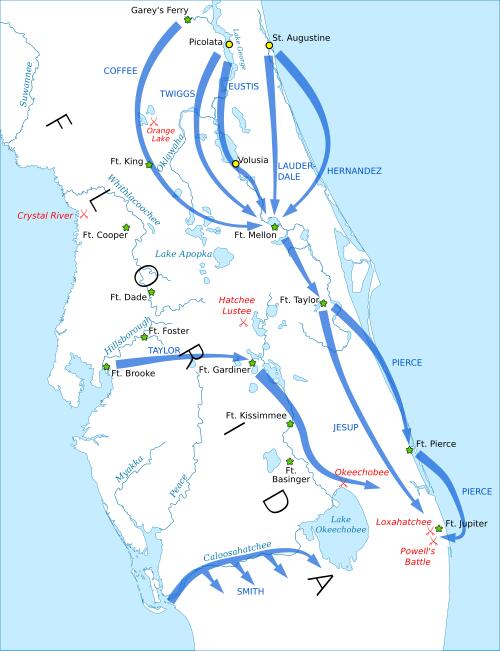
A number of American commanders failed. Normal Duncan Clinch achieved little and resigned. Normal Winfield Scott tried coordinated columns, however his forces could not navigate the swamps or discover the enemy.
Jesup modified techniques. He constructed forts and provide depots throughout Florida. His troops carried out raids to destroy Seminole villages, crops and cattle. They confiscated roughly 15,000 cattle from the Alachua area alone. They burned corn fields and meals shops. The technique aimed to starve the Seminoles into give up.
Main Ethan Allen Hitchcock served beneath Jesup. In February 1836, Hitchcock discovered the stays of Dade’s command.
In his journal, he wrote, “The federal government is within the fallacious, and that is the chief reason behind the persevering opposition of the Indians, who’ve nobly defended their nation towards our try and implement a fraudulent treaty.”
The conflict floor on by way of ambushes and small skirmishes. The Seminoles besieged most of the forts for weeks. In July 1836, warriors trapped American troopers in a Withlacoochee River blockhouse for 48 days. The troopers endured brutal warmth, illness and the fixed menace of demise.

Seize By way of Treachery
In September 1837, American troopers captured King Philip. Jesup had Philip ship a message to his son Coacoochee to rearrange a gathering. When Coacoochee arrived beneath a flag of truce, Jesup detained him. Coacoochee, additionally known as Wildcat, was a rising conflict chief and some of the distinguished leaders the U.S. sought to seize.
In October 1837, Osceola and one other chief requested a gathering with Jesup to debate peace. Once they arrived beneath a white flag, Jesup’s troops seized them. The American public condemned the violations. Jesup transferred Osceola to Fort Moultrie jail in South Carolina. Osceola refused to just accept any removing settlement.
On Jan. 30, 1838, he died at age 34 from throat irritation. The attending doctor beheaded his corpse.

Coacoochee was imprisoned at Fort Marion in St. Augustine. The fort was thought of escape-proof with five-foot-thick partitions and an previous Spanish moat. However Coacoochee and 19 different prisoners squeezed by way of a slender window of their cell.
He later recalled, “With a lot problem I succeeded in getting my head by way of; for the sharp stones took the pores and skin off my breast and again.” They descended by rope to freedom earlier than dawn.
Coacoochee’s escape energized the resistance. He turned the Seminoles’ most vital remaining chief. His band included a whole lot of Seminole and Black Seminole warriors. U.S. army information famous that when American troopers realized Coacoochee was in an space, they stopped their operations. His repute as a fierce warrior chief weighed closely on the troopers’ minds.

Christmas Day at Lake Okeechobee
Colonel Zachary Taylor led 800 troops towards Seminole and Miccosukee warriors on Christmas Day 1837. Between 380 and 480 warriors camped on Lake Okeechobee’s northeast shore. They positioned themselves in an space surrounded by sawgrass and dust. Coacoochee, Sam Jones and Alligator led the Seminole forces.
Taylor ordered a frontal assault. Missouri volunteers went in first. The soldiers opened hearth. The volunteers broke and fled. Colonel Richard Gentry fell mortally wounded.
Taylor despatched within the sixth Infantry. 5 corporations took devastating casualties within the sawgrass. Each officer however one died or was wounded. Most noncommissioned officers fell. Solely 4 males from these corporations survived unhurt.
The 4th Infantry lastly pushed the soldiers from their place. They escaped throughout the lake that evening. Taylor misplaced 28 killed and 112 wounded. The Seminoles left 12 lifeless. Later accounts from Native members indicated one other 11 had been wounded.
The American press known as it a terrific victory. Following this and his later service within the Mexican-American Warfare, Taylor turned a nationwide hero and finally president. Although he had suffered extreme casualties whereas killing comparatively few enemies in Florida. The Seminoles escaped deeper into the Everglades and saved preventing.

The Warfare Drags On
In March 1837, Chief Micanopy had agreed to cease preventing. Lots of of Seminoles gathered close to Fort Brooke to await transport west. However on June 2, warriors led by Sam Jones attacked and managed to free them. They disappeared into the wilderness.
This could go on for years. Teams of Seminoles would give up and collect earlier than being transported west. Then they might escape and rejoin the struggle. Others had been hunted down. Their villages had been destroyed.
Coacoochee fought on till 1841. When he lastly confronted seize once more, he mentioned, “I used to be in hopes I might be killed in battle, however a bullet by no means reached me.”
Earlier than his compelled removing to Oklahoma, he delivered a speech that captured what he believed the conflict had been about.
“I’ve mentioned I’m the enemy to the white man,” he mentioned. “I may reside in peace with them, however they first steal our cattle and horses, cheat us, and take our lands. The white males are as thick because the leaves within the hammock; they arrive upon us thicker yearly. They might shoot us, drive our girls and kids evening and day; they could chain our fingers and ft, however the crimson man’s coronary heart will likely be at all times free.”
The Warfare Ends
By 1842, the US had spent greater than $20 million preventing the Seminoles. That represented roughly 10 p.c of the federal funds. Greater than 1,500 troopers had died, largely from illness. Lots of of civilians additionally died. The federal government forcibly eliminated 3,000 Seminoles to Indian Territory in Oklahoma.
The nation was appalled on the final result.
However a number of hundred Seminoles remained on distant Everglades islands. The army by no means defeated them. On Aug. 14, 1842, the federal government declared the conflict over. No peace treaty was ever signed.
A third battle erupted in 1855. The ultimate Seminole Warfare lasted till 1858. Fixed army patrols and bounties decreased Florida’s Seminole inhabitants to roughly 200 people. The Seminoles who stayed by no means surrendered. They survived on land that white settlers thought of nugatory.
Their descendants fashioned the Seminole Tribe of Florida, which right this moment numbers greater than 4,000 members.

Troopers killed within the Dade Bloodbath and the next battles relaxation beneath three coquina pyramids at St. Augustine Nationwide Cemetery. Greater than 1,300 troopers are buried there. The cemetery dedication occurred on Aug. 14, 1842, the day the federal government declared the conflict over.
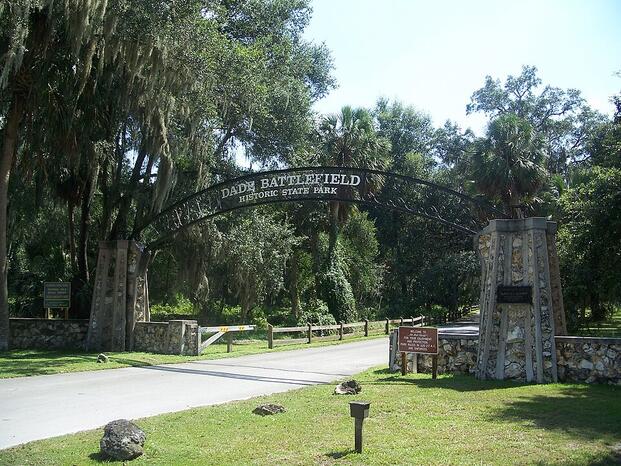
The Dade Battlefield Historic State Website close to Bushnell preserves the place Dade and his males died. Annual reenactments mark the anniversary. The positioning commemorates America’s longest and deadliest conflict towards the Native Individuals. It was a seven-year battle the US by no means really gained.
Story Continues






